Minnesota's Buffer Law was enacted to help keep Minnesota's water clean. Buffers are also known as a riparian filter strip adjacent to a stream, river, lake, or wetland. These buffers filter out phosphorus, nitrogen, and sediment. Studies completed by the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency show that buffers are critical to protecting and restoring water quality, natural stream functions, and aquatic habitat and life.
Buffers are required along public waterways and ditches. Public waterways include lakes, rivers, and streams. This type of waterway requires a 50-foot average buffer. Buffers of 16.5 feet are required along public ditches. The original buffer law was signed into law in 2015, and after several modifications, the deadline for implementation for public waterways was 2017 and 2018 for public ditches.
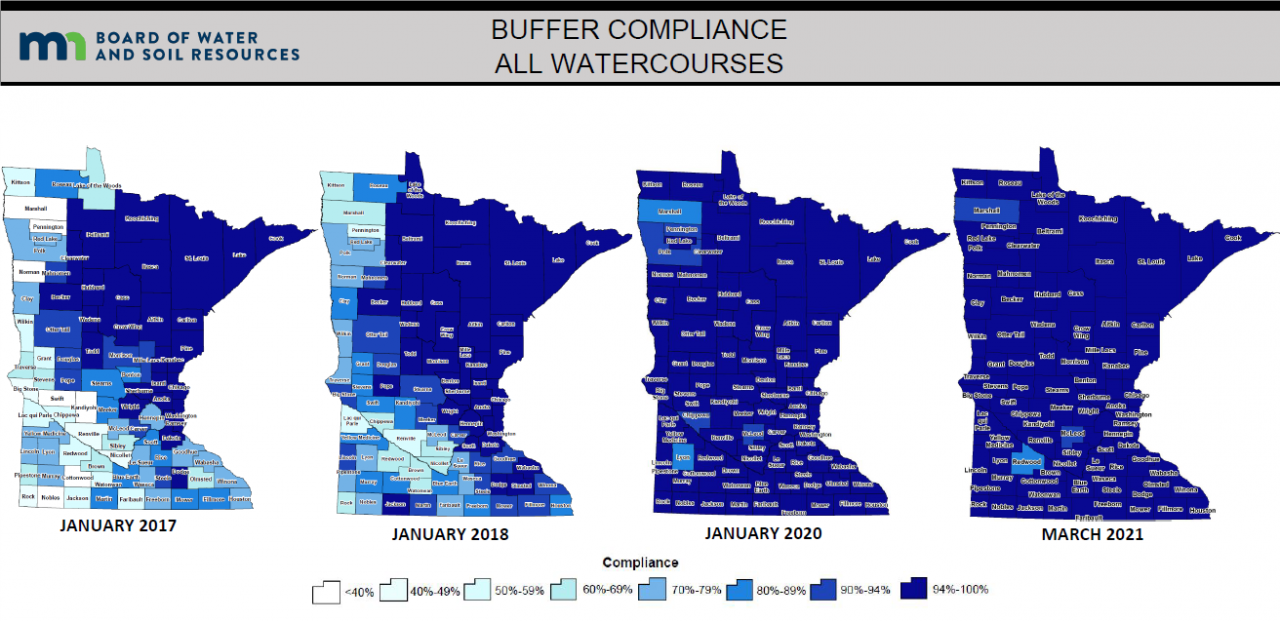
Buffers are required to be vegetated with perennials. This includes hay and forage crops such as alfalfa and clover, woody vegetation, perennial grains that can be harvested later, and prairie vegetation. This vegetation is key to helping keep Minnesota's water clean. Since 2017, soil and water conservation districts, including ACD, have worked hard to help bring all applicable parcels into compliance. The map below shows this hard work and that most of Minnesota are 94% to 100% compliant. For more information please contact Mollie Annen,