Non-native Phragmites is a highly invasive plant that can invade wetlands and shorelines, outcompete native vegetation, and degrade wildlife habitat. Fortunately, most of the infestations in Minnesota are small and there is hope that the invasive grass can be controlled.
Coon Creek Watershed District and ACD staff first detected non-native Phragmites in Anoka County in 2018 along the Ham Lake shoreline. The 2,500 square foot stand was herbicide treated in fall 2018 and mowed in January 2019. No Phragmites was found at the Ham Lake site in 2019 and 2020. One sprout of Phragmites was found in 2021 and dug up.
Additional non-native Phragmites infestations have been found and verified by UMN in Anoka County. The treatment success at Ham Lake inspired staff to continue additional efforts to control non-native Phragmites. In 2019, the Anoka County AIS Prevention grant paid for treatment of 14 additional Phragmites sites that were detected in the 2019 growing season.
The MN Department of Agriculture Noxious Weed grant provided funds for the Metro Counties to collaborate and treat over 80 sites in 2020 and 2021. The University of MN, MN DNR, and MN DOT are also tracking and treating additional sites throughout the state. Sites will continue to be monitored to determine treatment needs.
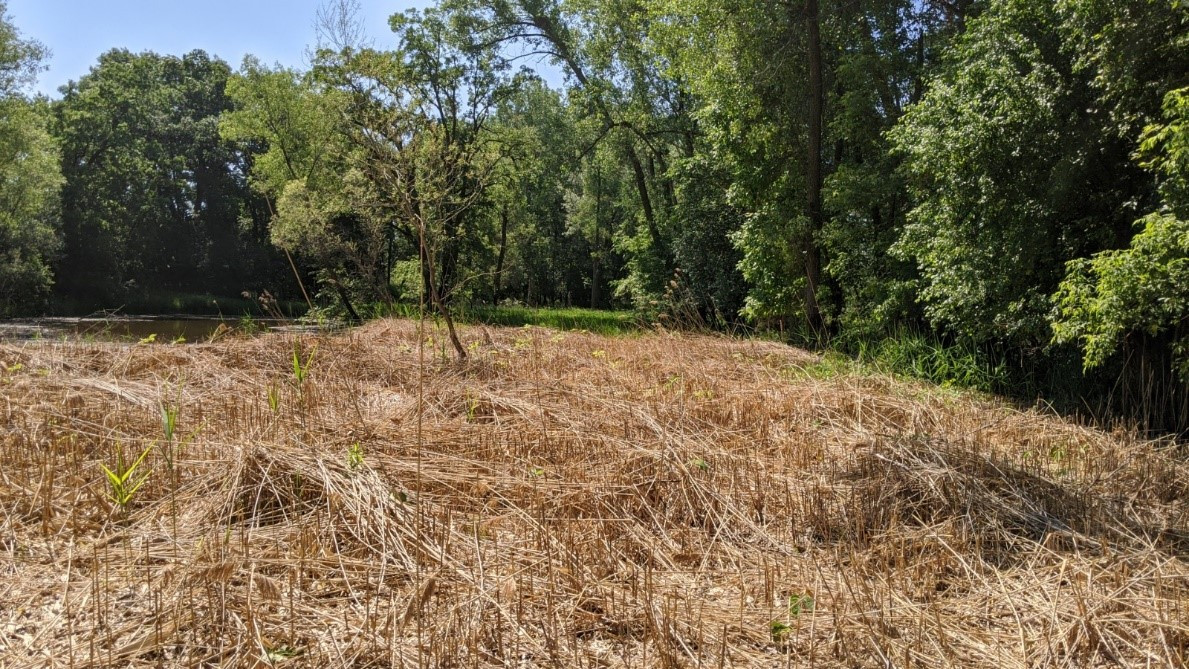
Photo below shows a stand of Phragmites at a site in Anoka County being monitored in 2020. Follow up treatment occurred in September 2021.
Find more information and distribution maps can be found at the links below:
https://www.eddmaps.org/distribution/viewmap.cfm?sub=59038
https://www.dnr.state.mn.us/invasives/aquaticplants/phragmites/index.html