Okay – the decay of organic materials in oxygen-poor shallow waters doesn't smell great. While this can worsen when nutrient pollution triggers excess algae growth, it is an otherwise natural process. Odor is a small price to pay for the vast benefits we receive from shallow lakes and wetlands; they retain floodwater and pollutants present in runoff, recharge groundwater, and provide fish and wildlife habitat that supports bountiful opportunities for hunting, fishing, bird-watching, and other outdoor recreation.
For many, the word "lake" triggers a vision of clear and deep water ideal for swimming and boating. However, over 5,000 of Minnesota's lakes larger than 50 acres are actually shallow lakes that are less than 15 feet deep and dominated by wetland habitat. In shallow lakes, sunlight reaching the lakebed, combined with readily available nutrients, increases the growth of aquatic plants. Shallow water also allows for more abundant emergent vegetation such as bulrush and cattails, which can extend well beyond the shoreline and even become dominant, especially during periods of drought. Mucky lakebed conditions are produced as large quantities of organic materials die, settle to the bottom, and decompose over time.
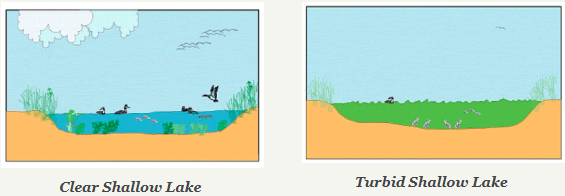
Shallow lakes can exist in one of two states: clear or turbid. Clear shallow lakes are dominated by submerged vegetation, which often grows densely and can reach the water's surface. These aquatic plants are a source of food and habitat for fish and wildlife such as amphibians, waterfowl, and invertebrates at the base of both aquatic and terrestrial food webs. On the flip side, turbid shallow lakes are dominated by algae, which clouds up the water and restricts the growth of submerged aquatic vegetation. Turbid lakes typically support fewer fish and wildlife due to the lack of habitat provided by aquatic plants.
Many shallow lakes are impacted by human activity, particularly those that are on the receiving end of stormwater and agricultural drainage networks. However, even the most impacted shallow lakes are still valuable and can surprise us, as the recent plant inventory of Highland Lake in Columbia Heights proved when an uncommon pondweed species was found.
Check out MNDNR Shallow Lakes Program for more information about shallow lakes. Also, here's a great video produced by Ramsey- Washington Metro Watershed District about Minnesota's shallow lakes.