The 2026 budget request to Anoka County includes adding a Groundwater Specialist to ACD's staff. This is the third consecutive year that this need has emerged as a top priority. Anoka County has never had a professional dedicated solely to managing our groundwater. Given our situation, it's time to shift our priorities. What situation?
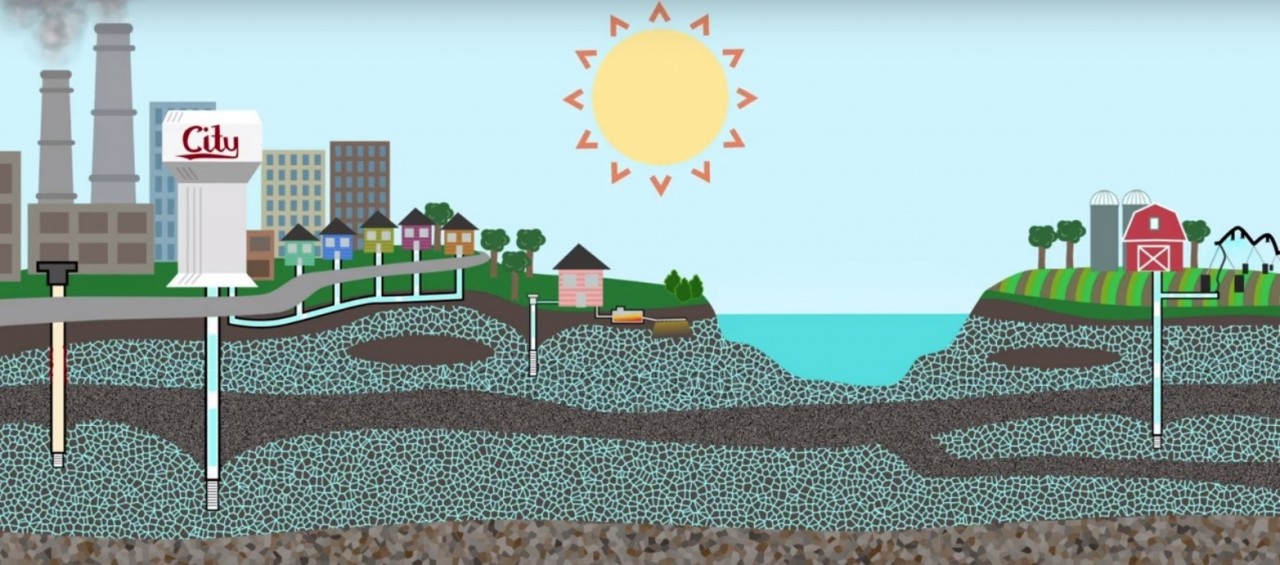
- 94% of us in Anoka County rely on groundwater for drinking and other needs
- We have more private wells than any other county in MN (53,000)
- We have more Superfunds sites than any other county in MN (9)
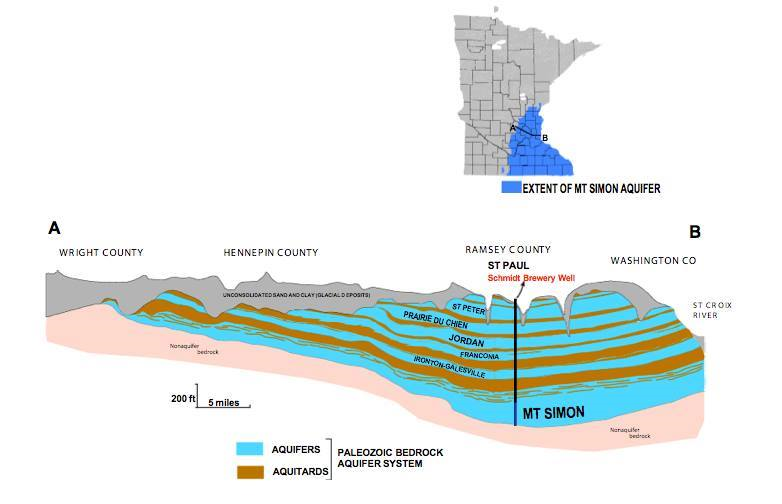
- We sit on the Anoka Sandplain, making our drinking water highly vulnerable to contamination
- Our shallow groundwater recharges aquifers relied on throughout the Metro Area.
This combination of factors can come together in troubling ways.
- Drinking water contamination in Andover neighborhoods near closed landfills.
- 47 private wells in Blaine and Ham Lake went dry due to interference from municipal well pumping in the City of Blaine. Three Blaine wells had to be shut down.
- "Forever chemicals" (PFAs) are showing up in groundwater across Minnesota, especially in Anoka County. Potential health ramifications are unknown.
- Drought diminished shallow groundwater, resulting in record-low lake and river levels.
- Multiple train derailments across the country exposed the vulnerability of drinking water to contamination by spills. Anoka County must be prepared to respond quickly to spills.
If only we had a Groundwater Specialist at ACD, we could:
- Develop a groundwater management plan and secure state approval,
- Secure $150K-$350K/year in state funds available to those with approved groundwater plans,
- Use advanced technology for high-resolution groundwater modeling,
- Analyze neglected datasets for hotspots and trends in groundwater degradation,
- Engage MPCA, MNDNR, and MDH to enhance the service Anoka County constituents receive,
- Coordinate regional planning, wellhead protection, and contamination response,
- Implement sentinel well monitoring,
- Manage cost-share programs for projects like septic upgrades, well sealing, and agricultural irrigation technology upgrades,
- Inform civic leaders, public employees and the public at large on groundwater, and
- Serve as the trusted expert on groundwater issues.
If groundwater is a mystery to you, please watch the short videos linked below, which were made locally and are often referenced nationally.
Groundwater - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gxENTkMmyEE
Groundwater Contamination - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gRSHJpe8pq8&t=12s