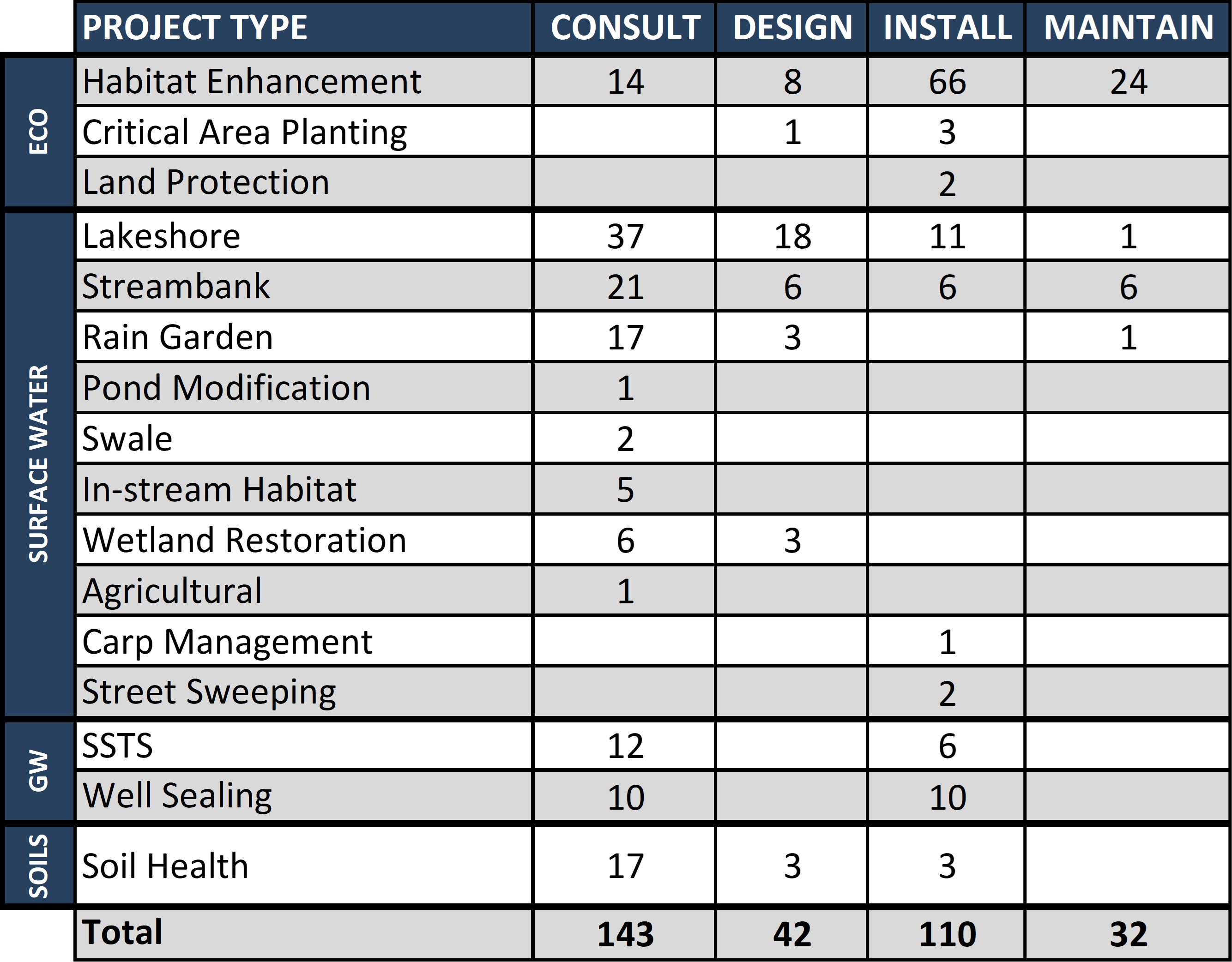
Each year, ACD staff provide technical assistance for projects focused on ecological resources, surface water, groundwater, and soils throughout Anoka County. This work includes ecological projects such as habitat enhancement and critical-area plantings; surface-water projects such as lakeshore improvements, rain gardens, and swales; groundwater protection through well sealing and septic-system upgrades; and soil-related practices such as cover cropping. These projects help enhance habitat, protect water quality, and support healthy natural systems.
Assistance typically begins with a site consultation. This includes a conversation with the landowner, a review of maps and available information about the property, and a site visit to walk the property and discuss options. If a project moves forward, ACD can assist with planning and design, provide installation oversight, and offer guidance on long-term maintenance. These efforts are made possible through collaboration with landowners and partner organizations. The table below summarizes the technical assistance provided by ACD staff in 2025.
If you have a conservation question or are interested in exploring options for your property, ACD staff are available to help! We look forward to continuing this work in 2026 and supporting positive environmental outcomes throughout Anoka County. For more information, contact Mitch Haustein, Stormwater & Shoreland Specialist, at