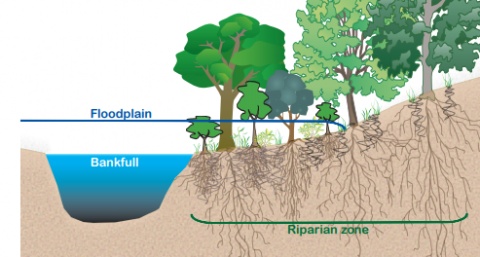
Vernal pools are shallow wooded wetlands that fill with water in the spring and fall, then dry out in the summer. They may simply look like a large muddy puddle, but in reality these small depressions are filled with life and benefit local water quality.
By capturing water from snowmelt and heavy rains, vernal pools reduce the amount of runoff – and the contaminants it carries – reaching nearby surface waters and developed lands. This lowers flooding risks, improves water quality, and contributes to groundwater recharge as the trapped water slowly infiltrates through the soil.
- Aquatic Invertebrates and Amphibians
Vernal pools rarely contain fish because their water levels fluctuate dramatically. This provides a safe haven for many invertebrate and amphibian species that would otherwise be heavily predated upon. Many depend on vernal pools during their egg and larval stages, leaving for nearby aquatic and terrestrial habitats once fully developed. Others spend their entire life within or near the wetland's depression.
- Birds, Reptiles, and Mammals
Due to their abundance of amphibians and invertebrates, vernal pools supplement the food and water needs of wildlife such as waterfowl, songbirds, turtles, snakes, bats, and even bears. These benefits stem beyond the vernal pool itself when many of the invertebrates transition from aquatic larvae to terrestrial adults, serving as forage for insectivore species.
Explore and Protect
Vernal pools are highly sensitive to changes in vegetation cover, climate, and local topography. Because they are nearly invisible for much of the summer, they can be easily missed and destroyed if the land is modified; even an unintentional pass through these depressions during an ATV ride can strongly impact their function.
Seasonal wetlands like vernal pools are regulated under the Minnesota Wetland Conservation Act (WCA). You can prevent impacts to vernal pools on your property by marking their boundaries when visible in the spring and avoiding disturbance throughout the year. This is also a great time to explore the abundance of wildlife in and around these wetlands – an especially popular adventure for children.
Additional Resources
"Spring-to-Life Ponds": an Illustrated Learning Guide, produced by the MNDNR
MN Frog ID and Calls and Common Vernal Pool Invertebrates, produced by the MPCA and University of Wisconsin
Locating and Protecting Vernal Pools, produced by the MN Land Trust